We may earn revenue from the products available on this page and participate in affiliate programs. Learn More ›
Dependable air conditioning is essential for keeping comfortable during the sweltering days of summer, so homeowners should be sure to assess their HVAC needs (and meet them!) before temperatures climb. Whether your existing central AC is on its last leg or you’ve just put on an addition that needs cooling, you’ll have a range of options available. And because you typically shop for air conditioners only once every decade or so (if you’re lucky), the marketplace is bound to have changed and expanded since the last time you looked. It’s important that you understand your needs and know what type of product will best meet those needs. “After all, selecting an air conditioner should not be viewed as a one-size-fits-all decision,” says Daniel O’Brian, technical expert for the online HVAC and plumbing retailer SupplyHouse.com.
Different types of air conditioners—such as central air conditioners, mini-splits, window units, and packaged terminal air conditioners (PTACs)—are designed for different living situations. “It’s important to look at a host of factors, such as the room or building itself, your budget, and the long-term plans for the space,” O’Brian says. With his assistance, we’ve put together a guide to different types of air-conditioning units so you can be sure to select the right one to suit your needs.

If Your Central Air Conditioner Is On the Fritz…
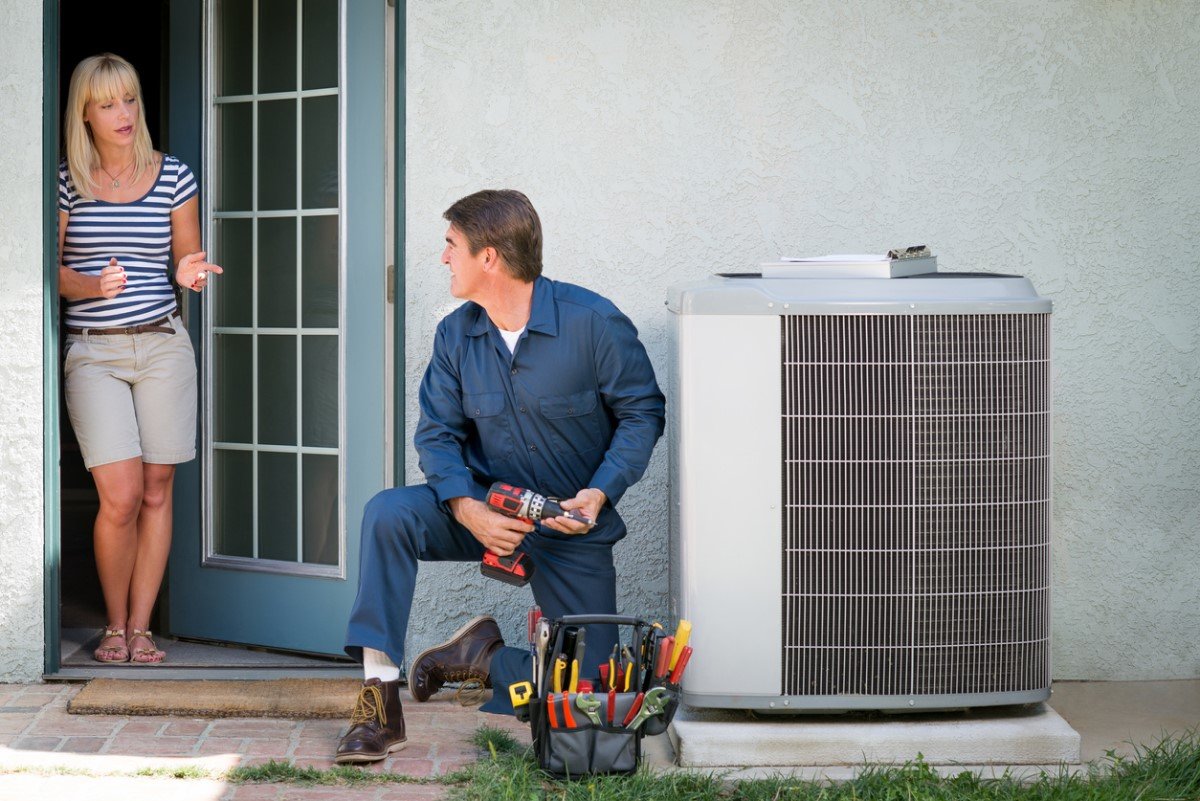
If you haven’t updated the central air conditioning that came with your home when you bought it, it’s easy to lose track of its age. You may have no idea just how many good years it has left. Most air conditioners do their best, most efficient cooling for about 10 years. After that, homeowners may notice higher utility bills, reduced airflow from the vents, increased indoor humidity, and even grinding noises when the AC kicks on.
These signs, in addition to the actual age of the air conditioner, can be indications that the unit is reaching the end of its useful life. If your appliance has reached double digits, it’s probably time to think about replacing the old unit with a new model, such as Goodman’s 1.5 Ton 16 SEER Central Air Conditioner (available from SupplyHouse).
Because installing this type of air conditioner requires that refrigerant lines be connected, in most states an HVAC pro will need to perform the installation. It’s wise to consult an expert before you buy, too, to help you determine the proper size unit for the size and configuration of your home. You want an air conditioner that’s big enough to effectively cool your home, but not too big. Buying an oversize unit “can cause inefficient use of electricity and cause the space to be cooled very quickly—so quickly that the system may not run long enough to dehumidify the room sufficiently,” O’Brian explains. Remember, in addition to cooling the air, an AC unit draws excess moisture out, which increases indoor comfort. With a new central air conditioner in place, you should experience an immediate improvement in both the comfort level in your home and the cost of your utility bills.
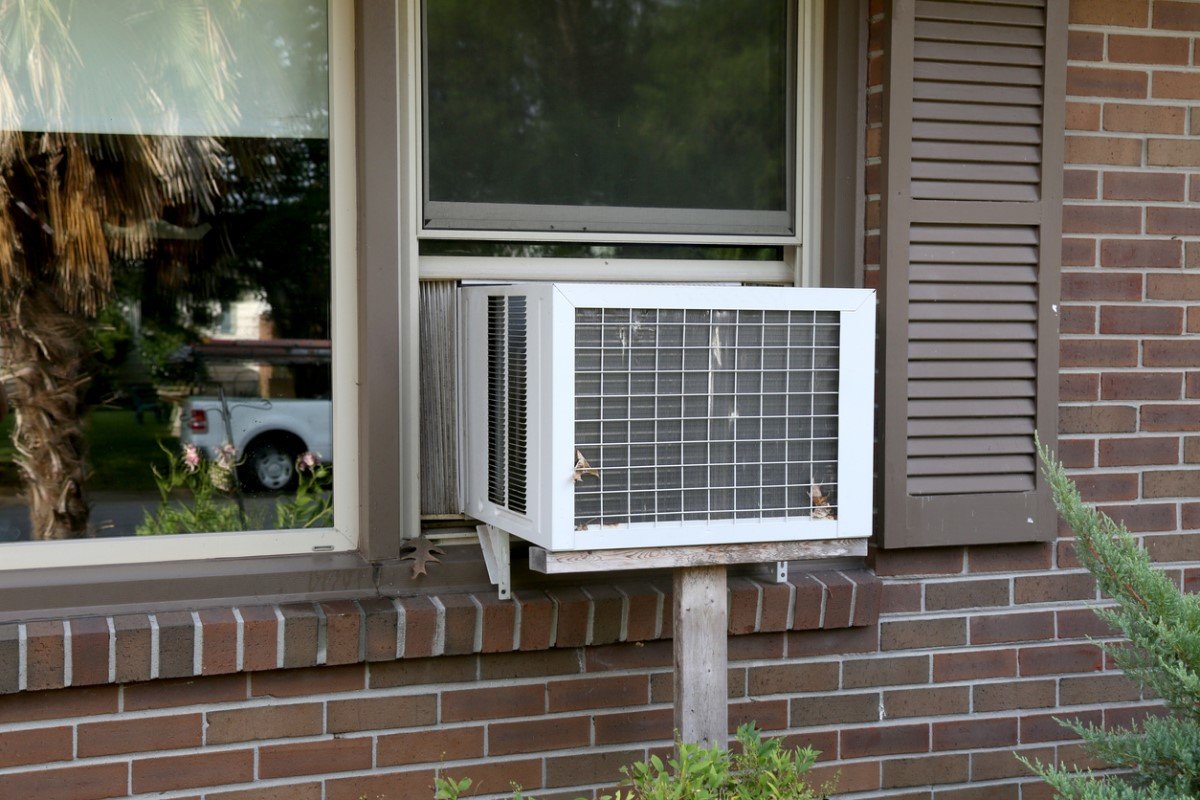

If You’re Cooling a Rental Property…
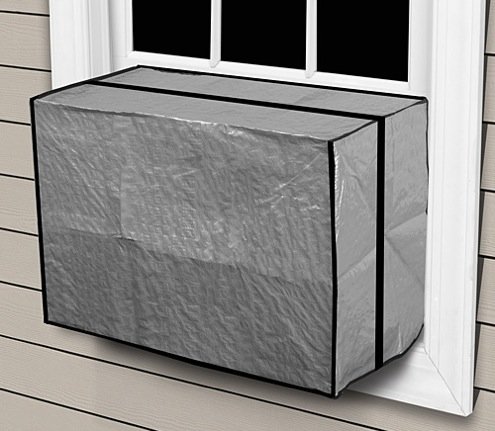
Buying an inexpensive home to serve as a rental can be a great investment, and air conditioning can make that property even more appealing to potential renters. But if your rental property doesn’t already have central air conditioning, you might have to spend big bucks to have ducts and a new system installed. In an effort to keep costs down, many owners of rental properties rely instead on window air conditioners or PTACs.
Window air conditioners are a good option—at least when there’s a window to start with. But in a room without a window, or with a fixed or small window that can’t accommodate a window unit, a PTAC can save the day. If you’re not familiar with PTACs, picture the air conditioners used by many large hotel chains—those rectangular units that sit along an exterior wall, just a few inches above the floor. As with window air conditioners, the temperature controls are located on the face of the unit.
“PTAC units are increasingly popular with landlords,” O’Brian says, adding that “they offer an affordable solution with no need to run any ductwork.” Because both window units and PTACs are self-contained (the compressor is inside the unit, not located outside as it is in a central air-conditioning system), they typically produce some noise during operation. Today’s models, such as the LG 10,2000 BTU Packaged Air Conditioner (available from SupplyHouse) are much quieter than those of even 10 years ago. Most emit barely a hum!
While setting up a window air conditioner is usually a DIY project, installing a PTAC is more complicated. It requires removing a section of the exterior wall and framing a rough opening to support the new unit. A homeowner who possesses basic carpentry and framing skills may feel inclined to take on the installation, but the average homeowner will probably want to hire a professional. One thing’s for sure: You should always contact your local building authority to see if you need to pull a permit before you start.

If You’re Trying to Cool a New Addition to Your House…
With residential real estate costs rising, many homeowners are opting to add to their existing home rather than buying a bigger house or having a new one built. Additions provide much-needed living space and can do wonders to open up a floor plan, but finding a way to keep them cool during hot weather can be tricky. For instance, perhaps it wasn’t possible to access and tie into the home’s existing central-air system during the construction process, or maybe the current system is not adequately sized for the additional ductwork.
In this scenario, the best type of AC unit is a ductless mini-split air conditioner, such as the super-efficient Comfort-Aire DV-Series Ductless Mini-Split Air Conditioner (available from SupplyHouse). “Ductless mini-split systems offer a great solution for room additions,” O’Brian says. Their biggest perk is that, as with a central air-conditioning system, the compressor is located outdoors, which allows for virtually silent operation. Mini-splits are typically located along the upper edge of an exterior wall. Installing them, however, is not a DIY project. Like central AC systems, mini-splits require the connection of refrigerant lines, which means an HVAC pro must do the work.
This article has been brought to you by SupplyHouse.com. Its facts and opinions are those of BobVila.com.