We may earn revenue from the products available on this page and participate in affiliate programs. Learn More ›
Highlights
- The average cost for electrician school ranges between $3,000 and $19,000.
- The main factors that affect how much a student will pay for electrician school include tuition fees, the type of school and program, the purchase of tools and equipment, and the cost of textbooks.
- Although attending electrician school isn’t a required step toward becoming an electrician, it offers numerous benefits. These include well-rounded instruction, the ability to specialize, the opportunity to network with other electricians, and in some cases, flexible scheduling.
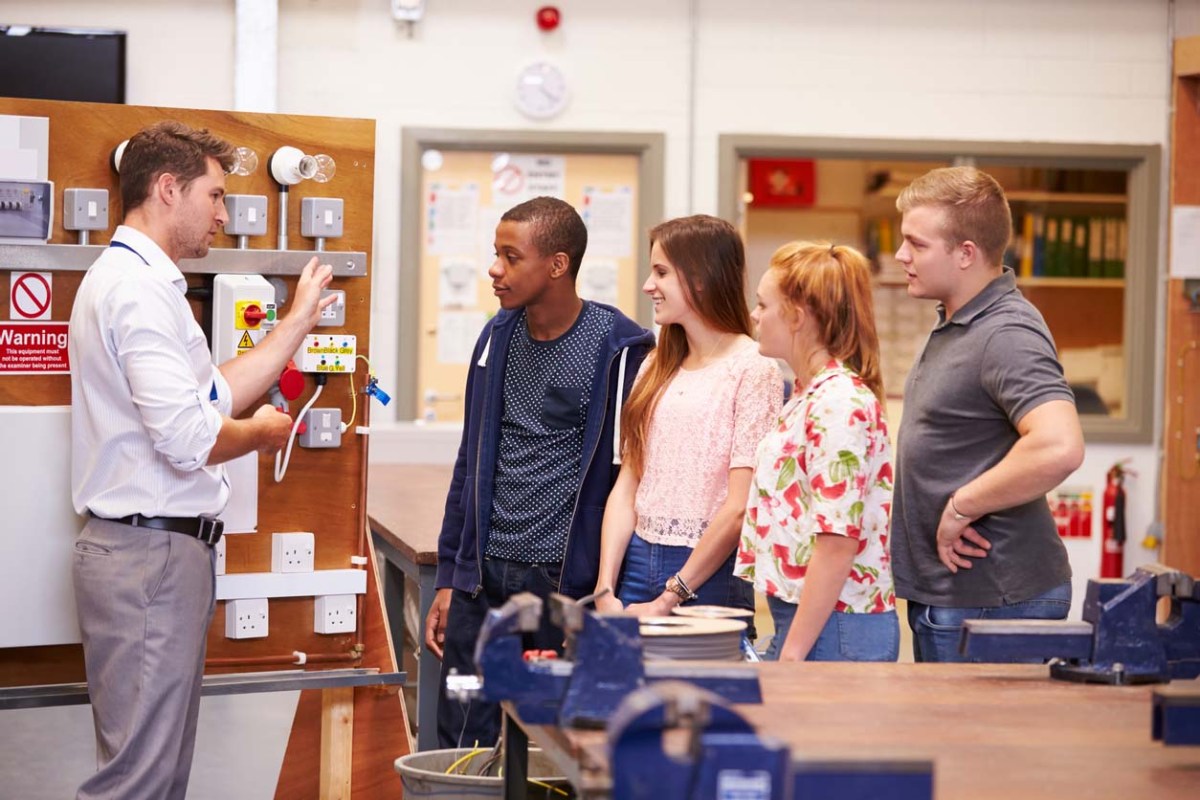
Starting a career in the electrical trade often begins with attending electrician trade school. Although there’s no nationwide education requirement to become an electrician, attending electrician school while working as an apprentice can give a student an edge when applying for jobs down the road. The cost of electrician training programs varies, but on average it can range from $3,000 to $19,000 depending on factors such as location, the type of school, and the duration of the program. Trade schools for electricians offer specialized courses designed to prepare students with necessary skills to work as an electrician. Electrician schooling costs typically include tuition fees, materials, and additional expenses such as tools or certification exams.
Many aspiring electricians opt for online electrician school, which provides flexibility to balance learning with other day-to-day commitments. Electrician vocational schools offer comprehensive programs, and the best electrician schools are recognized for producing skilled professionals. The duration of an electrician program varies, with options ranging from a short 3-month electrician course to more extensive programs that can take years. While electrician degree online programs exist, the emphasis is often on practical skills gained through hands-on training. As aspiring electricians consider pursuing an electrician certification program, evaluating the overall electrician school cost is a key component to making an informed decision.
Factors in Calculating Electrician School Cost
Those considering a career as an electrician will want to take into account the cost of attending an electrical trade school. The factors involved in calculating this cost can vary depending on tuition fees, school and program type, tools and equipment, and textbooks. On average, the cost for electrician training ranges from $3,000 to $19,000, but these figures can vary greatly based on local averages.
Tuition Fees
Electrician school tuition makes up a significant portion of the total expenses for students attending electrician training programs. The tuition cost can vary widely among different institutions based on regional economic conditions and the scope of the program.
Highly regarded electrician vocational schools or those offering extensive hands-on training may have higher tuition fees. On the other hand, more budget-friendly options may be available in the form of a local electrician’s course. Prospective students will benefit from carefully weighing the advantages of the program against the associated tuition costs to make sure they’re investing in an education that aligns with their career goals.
School and Program Type
When it comes to electrician schools, there are several options to consider. These can range from vocational and technical schools to community colleges and trade schools. Each type of school has its own advantages and disadvantages, and these factors can influence the cost of education.
- Vocational or technical schools. Vocational or technical schools can be an excellent option for those looking to become electricians. These schools usually provide hands-on training with smaller class sizes, which can allow for more individualized attention. The cost to attend vocational schools tends to be higher than that of community colleges. The costs associated with these schools can include tuition, lab fees, textbooks, and any specialized tools required.
- Community colleges. Community colleges offer electrician programs that are more affordable in comparison to those offered through vocational schools. Many offer certificate or associate degree programs, giving students a comprehensive education in electrical systems. In addition to lower tuition fees, community colleges can also provide flexibility in scheduling, making it easier for working professionals or those with family obligations to pursue a career in electrical work.
The specific electrician program chosen can also impact the cost of education. Programs can range from basic introductory courses to comprehensive apprenticeships, each with its own cost structure. Some of the most common ways to obtain electrician training include earning an associate’s degree or bachelor’s degree, taking certification exams, going through an electrical apprenticeship, or having military training.
Tools and Equipment
In addition to tuition fees, prospective students need to consider the expenses of acquiring the necessary tools and equipment essential for hands-on training and future professional practice.
Electrician training programs often require students to invest in a set of the best electrician tools that align with industry standards. These tools may include items such as pliers, wire strippers, voltage testers, and power drills. The cost of these tools can vary, but on average they cost approximately $2,500, and students will need to be prepared to budget for these essential items.
The electrician school length—whether it’s a shorter course or a more comprehensive program—can influence the types of tools required. Aspiring electricians will want to factor in the cost of these tools when determining how much they’ll spend on their education.
Textbooks
Textbooks are a significant factor in calculating the cost of attending electrician school. Similar to other degree or certification programs, electrician training requires students to purchase textbooks and reference materials that are essential for coursework and understanding industry standards.
The cost of textbooks can vary based on the specific curriculum of the electrician program and the type of school. Some programs may have comprehensive textbooks or digital resources tailored to the coursework, while others may rely on a combination of general and specialized materials. On average, the cost for textbooks is in the $1,100 range, but this depends on the length of the program and required materials.
Prospective students may want to consider putting aside funds for textbooks when budgeting for electrician schooling costs. It’s recommended that they also ask about textbook requirements for their program and explore potential cost-saving options, such as used books or digital downloads.
Additional Costs and Considerations
Beyond tuition, tools, and textbooks, several additional factors contribute to the total cost of attending electrician school. Students will need to consider certification and licensing fees, living expenses, the cost of ongoing education, and how geographic location can have an impact on these costs.
Certification and Licensing Fees
While many individuals may focus solely on tuition fees when calculating electrician school costs, it’s also important that they account for certification and licensing fees. These additional expenses can significantly impact the overall financial investment in becoming a qualified electrician.
Certification and licensing are essential requirements for electricians, since they need to meet the necessary standards and possess the skills needed to work safely as an electrician. Obtaining certification demonstrates to employers and clients that an electrician has undergone the proper training and possesses the competence needed to perform the job effectively.
Certification fees can vary depending on the specific type of certification and the governing body responsible for issuing it. In the United States, electricians typically need to pass a state-specific licensing exam. These exams, administered by state licensing boards, often come with application fees that vary depending on the state. Electricians typically spend between $15 and $75 per year for their license and from $30 to $75 for professional certification exams. Aspiring electricians can find out the specific details regarding licensing fees in their city, county, and state by contacting the appropriate officials.
Living Expenses
While tuition fees and study materials are typically the first expenses that come to mind, students will also want to consider the costs associated with daily living. These living expenses can affect the overall cost of attending school, and it’s crucial for aspiring electricians to take them into account.
- Accommodations. One of the key components of living expenses is accommodation. Whether it’s renting a room, sharing an apartment, or living on campus, finding a place to live is a necessary cost for any student. The cost of accommodations can vary significantly depending on the location of the electrician school. Attending school in a densely populated urban area will be more expensive compared to the cost of attending school in a more rural setting. Students will want to research average rental prices in the area and factor that into their budget.
- Food. Food is another major cost that cannot be overlooked. Electrician school typically involves full-time study, leaving little time for a part-time job. This means that students must rely on savings, financial aid, or loans to cover their food expenses. Prospective students will want to determine whether the school offers meal plans or if it’ll be necessary to budget for grocery shopping and cooking at home.
- Transportation. Transportation is another important expense. Commuting to and from electrician school can add up quickly, especially if the school is far from home. Whether by public transportation, owning a car, or utilizing rideshare services, students need to factor in the cost of transportation when calculating their overall expenses. Students might also need to consider the cost of traveling to and from apprenticeships or jobsites during their studies.
- Personal expenses. Students will also want to consider personal expenses such as health insurance, utilities, and leisure activities. While these expenses may seem insignificant individually, they can add up and affect the overall cost of attending electrician school.
- Emergency expenses. Students will want to keep unforeseen expenses, such as medical emergencies or unexpected repairs, in mind. It’s always recommended to have an emergency fund or some savings to cover unexpected expenses without having to rely on loans or credit cards.
Geographic Location
When prospective students are considering a career as an electrician, one important factor that often gets overlooked is the student’s geographic location. Where a student chooses to study can significantly affect the cost of attending an electrician school.
- Tuition fees. One of the most significant aspects affected by geographic location is the tuition fees charged by different electrician schools. Just like any other educational institution, schools in different regions have varying cost structures. Urban areas tend to have higher tuition fees due to the increased cost of living associated with densely populated areas. On the other hand, schools in more rural areas or smaller towns often offer lower tuition rates.
- Cost of living. The cost of living in a particular geographic location determines the expenses for housing, transportation, food, and other daily necessities. When evaluating different electrician schools, it’s important for students to consider the cost of living in the area where the school is located. The higher the cost of living in a region, the more expensive it will be to cover basic daily needs throughout the length of the electrical training program.
- Scholarships and grants. Geographic location can also affect the availability and eligibility criteria for scholarships and grants. Some states have specific funding programs or scholarships offered only to residents. Opting for an electrician school within the student’s state of residence may increase the student’s chances of obtaining financial aid specifically tailored toward local students. Certain regions may offer grants to encourage students to pursue careers in high-demand fields such as electrical work.
- Job market. Considering the job market opportunities is crucial when a prospective student is calculating the cost of attending an electrician school. Different regions may have varying demand for electricians, which affects employment prospects and potential salaries. Opting for a school in an area with a high demand for electricians can increase a student’s chances of finding a job upon graduation.
- Licensing requirements. Each state or region has its own licensing requirements and regulations for electricians. It can be advantageous for a student to attend electrician school in the same state where they plan to work, since the curriculum may align with the specific licensing requirements of the area. This can potentially save time and money, since the student will not have to take additional courses or exams to meet the local requirements.
Ongoing Education
The dynamic nature of the electrical trade demands that professionals stay current with industry advancements and updates throughout their careers. Budgeting for ongoing education is important for electricians seeking to enhance their skills, stay competitive in the job market, and meet evolving industry standards.
Many electrician licensing bodies and associations require electricians to complete a certain number of continuing education credits to maintain their professional licenses or certifications. These credits typically involve attending workshops, seminars, or courses that cover topics such as electrical code updates, new equipment, and emerging techniques. These educational opportunities often come with a cost, either in terms of registration fees, travel expenses, or time off from work.
Electricians who want to excel in their careers often choose to pursue specialized certifications or advanced courses to expand their knowledge and skills in niche areas. These specialized certifications often require additional training, examinations, and fees. By investing in these additional educational opportunities, electricians can enhance their careers and potentially command higher salaries.

Electrician School Cost by Type of Program
The cost of electrician school can vary significantly based on the type of program chosen, with each offering distinct advantages and unique considerations.
Associate Degree
Earning an associate degree in electrical technology provides students with a broader education compared with obtaining a diploma or completing a certification program. These programs typically include both technical coursework and general education classes, giving students a well-rounded background. In addition to courses focused on electrical theory, wiring techniques, circuitry, and safety, associate degree programs often include classes in subjects such as mathematics, communication, and computer literacy. This wide-ranging education provides students with additional skills and knowledge that are valuable in their future careers.
Another significant advantage of earning an associate degree is the enhanced job prospects that accompany it. While a diploma or certification may be sufficient for securing an entry-level position as an electrician, an associate degree can set candidates apart from the competition. Many employers value the broader skill set and comprehensive training that comes with a degree, making those with this qualification more desirable in the job market.
Bachelor’s Degree
It’s important to note that becoming an electrician typically does not require a bachelor’s degree. Many electricians enter the workforce after completing an apprenticeship program or obtaining a relevant associate degree or diploma. For those who aspire to advance their careers, a bachelor’s degree can offer unique advantages.
When calculating the cost of electrician school, it’s important for students to examine various factors such as tuition, materials, and the duration of the program. Earning a bachelor’s degree often involves higher tuition bills than for a diploma or associate degree. A bachelor’s degree program often takes 4 years, whereas other educational options have shorter durations.
The higher cost and longer duration of a bachelor’s degree program can provide some benefits.
- Expanded skills and knowledge. A bachelor’s degree program offers a comprehensive curriculum that delves deeper into the theoretical aspects of electrical engineering, mathematics, and other related subjects. This expanded knowledge and skill set can provide students with a competitive edge in the job market and enable them to tackle complex jobs with confidence.
- Professional development opportunities. Bachelor’s degree programs often provide opportunities for internships, co-op experiences, or research projects. These experiences can help students gain practical, hands-on knowledge and make valuable industry connections. Some colleges and universities may have partnerships with local businesses, providing students with potential job opportunities upon graduation.
- Leadership and management roles. With a bachelor’s degree, graduates may develop the necessary skills to pursue leadership or management roles within the electrical industry. Whether it’s overseeing a team of electricians or managing large-scale projects, professionals who have a bachelor’s degree can enhance their abilities and increase their chances of climbing the career ladder.
Certification
Aspiring electricians who want the shortest program often find that obtaining a certificate from a trade school is the way to go. These programs can last from a few months to a year, and students who earn a certificate often experience more productive apprenticeships. Advanced certification is an additional credential that demonstrates a higher level of knowledge and proficiency in the field. In the electrical industry, certification is often a requirement for higher-level positions, such as becoming a journeyman electrician or electrical contractor. These roles not only come with increased responsibilities but also offer higher salaries.
Earning a certification can also open doors to specialized fields within electrical work. Electricians who specialize in areas such as industrial automation, solar energy, or low-voltage systems are in high demand and command higher salaries than general electricians. These specialized certifications require additional training and exams, but they can lead to increased earning potential and more job prospects.
Electrical Apprenticeship
Apprentices learn their trade as an assistant to a master or a journeyman electrician. Some common tasks involve carrying supplies and tools to worksites and performing some minor repairs. Students who are also apprentices can earn money while learning, which can offset some of the training costs. Apprentices make an average of $15.43 per hour, which is relatively low. There’s a potential to make extra money through commissions and bonuses, which can increase the pay by $2,000 per year. Electricians are required to apprentice, even if they’ve earned a certificate or degree. Those who have completed a degree program or earned a certificate will often find that some of those credits will go toward the apprenticeship requirements.
Students can become apprentices through a union or non-union training program. Many union programs are organized through a partnership with the National Electrical Contractors Association (NECA) or the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers (IBEW). The two unions, when joined with local contractors, form the Electrical Training Alliance partnership.
Apprenticeships that are not organized by a union are called merit-based or open-shop apprenticeships. These non-union apprenticeships can be found by contacting local non-union electricians in the student’s area, and the overall costs are similar to those of union-based apprenticeships.
Electricians begin their careers as an apprentice, either after finishing a training program or delving right in. They learn their trade as an assistant working under the strict supervision of a master-level electrician. On average, a student spends about 4 or 5 years as an apprentice, and then will earn their credentials by passing an exam and applying for a license. For those who want to apply to be an electrical contractor or a master electrician, a 2-year waiting period is enforced until they can pass an oral or written exam that’s organized based on the National Electrical Code and local building codes.
Military Training
Some people choose to serve in the military before transitioning to a civilian career. The skills and knowledge acquired during military service often make veterans highly sought after by employers. This can be particularly true for technical professions such as electricians, where discipline, attention to detail, and problem-solving skills are important. Some military branches offer electrician training programs as part of their education and vocational training initiatives. These programs provide veterans with a solid foundation in electrical work and provide practical experience.
Veterans may be eligible for educational benefits provided by the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). Benefits such as the GI bill can help cover a portion or sometimes the entire cost of electrician school tuition.
Benefits of Choosing to Go to Electrician School
Attending electrician school provides students with a multitude of benefits that can lay the foundation for a successful career as an electrician. Some advantages of choosing electrician school are flexibility in scheduling, a well-rounded instruction, specialization, and networking.
Flexibility
Flexibility is a significant benefit of attending electrician school, offering students the opportunity to tailor their education to fit their schedule. Many electrician programs provide flexible scheduling options, including evening classes, weekend sessions, or online courses. The adaptability allows students to balance their education with other commitments, such as work or family responsibilities.
Well-Rounded Instruction
Well-rounded instruction is another advantage of attending electrician school, providing students with a comprehensive and balanced education in the trade. Electrician programs cover not only theoretical knowledge but also practical skills that are essential for success in the field. From understanding electrical theories to hands-on training with tools and equipment, students gain a holistic understanding of the profession.
Specialization
Specialization allows students to focus on specific areas of interest in the electrical trade. Electrician programs often offer diverse courses that enable students to focus on specific topics, such as renewable energy systems, industrial wiring, or automation technology. This type of specialized education allows students to tailor their education according to what they’re interested in, and it also enhances expertise in niche areas of the field. Specialization can open doors to unique career opportunities, making graduates more competitive in the job market.
Networking
Networking is a valuable benefit of attending electrician school, creating opportunities for students to connect with industry professionals and peers. Electrician programs often organize networking through events, workshops, and partnerships with local businesses. Building relationships with experienced professionals can offer students insights into the industry, potential job opportunities, and guidance for career growth. Connecting with classmates can help students develop a supportive community that can provide collaborative learning experiences and future professional partnerships.

How to Save Money on Electrician School Cost
Electrician school can be a great investment for those looking to start a rewarding career as an electrician, but the cost of tuition and tools can sometimes be a barrier for many. Luckily, there are various ways to save money on electrician school costs.
- Research scholarship and grant options. Many organizations offer scholarships and grants specifically for students pursuing electrician training.
- Compare and contrast. Compare the tuition fees of different electrician schools in the area. Some institutions may offer more affordable programs without compromising the quality of education.
- Consider online courses. The best online electrician schools often have lower tuition costs compared with those of traditional in-person courses. This option allows students to save money on commuting and housing expenses as well.
- Buy used. Instead of purchasing brand-new textbooks and tools, consider buying second-hand. Look for online marketplaces or ask former students if they have any materials they’d be willing to sell.
- Take advantage of tax credits. Ask at the local tax office if there are any available tax credits for vocational training. This can help offset the cost of tuition.
- Look for free or low-cost resources. Explore free or low-cost resources online to supplement in-class learning, such as tutorials, forums, or industry publications.
Questions to Ask About Electrician School
When students are considering attending electrician school, asking the right questions is an important step before making a big decision.
- Is the school accredited?
- What is the curriculum like?
- What are the specific courses offered in the program?
- What type of degree or certificate will I earn?
- Will this school prepare me for the specific type of electrical work I’m interested in?
- How long does the program take to complete?
- Does the school require a high school diploma or equivalent?
- Does the program offer hands-on training?
- What is the availability of labs, workshops, and apprenticeship programs?
- What is the student-to-instructor ratio?
- Will the program assist with job placement?
- Does the school have connections with local employers?
- Will I have to find my own apprenticeship, or does the school have apprenticeship opportunities?
FAQs
Attending electrician school can open many doors to a successful career. Those interested in the cost of tuition, average salary ranges, training duration, and earning potential will want to review the following frequently asked questions and their answers.
Q. Which electricians have the highest salary?
Some of the highest-paying electrician jobs include Senior Electrical Estimator ($103,000 to $135,000 per year), Senior Electrical Designer ($83,500 to $124,000 per year), Electrical Estimator ($75,000 to $113,000 per year), and High Voltage Electrician ($61,000 to $108,500 per year).
Overall, the cost to hire an electrician ranges from $162 to $535, with many homeowners spending an average of $346. For those interested in hiring an electrician, search online for “how to hire an electrician near me” to find a professional.
Q. How long does electrician school take?
Many trade schools take less than 2 years to complete, and many have training programs that last as little as 8 to 9 months.
Q. Can you make money as an electrician while in school?
Students who are completing their apprenticeship while in electrical school often make money while going through their hands-on training.
Sources: RSI: The Refrigeration School, Electrical Career Now, ElectricalSchool.org, Indeed, ZipRecruiter, Center for Employment Training

















