

We may earn revenue from the products available on this page and participate in affiliate programs. Learn More ›
Whether you own your own home or are renting from a landlord, you have a lot to stay on top of. Among other things, you need to keep your appliances functioning properly and operating efficiently, adjust the thermostat to maximize comfort and energy savings, and make sure that monitors and alarms are set up correctly to keep you and your loved ones safe. Juggling these tasks and staying up to date on best practices can be challenging. Consult the guide below to help you focus on the numbers that matter the most, including the ideal thermostat setting, unsafe radon levels that require remediation, the ideal SEER ratings for an air conditioner or HVAC system, and more.
RELATED: What Temperature Should I Set My Thermostat in Winter?
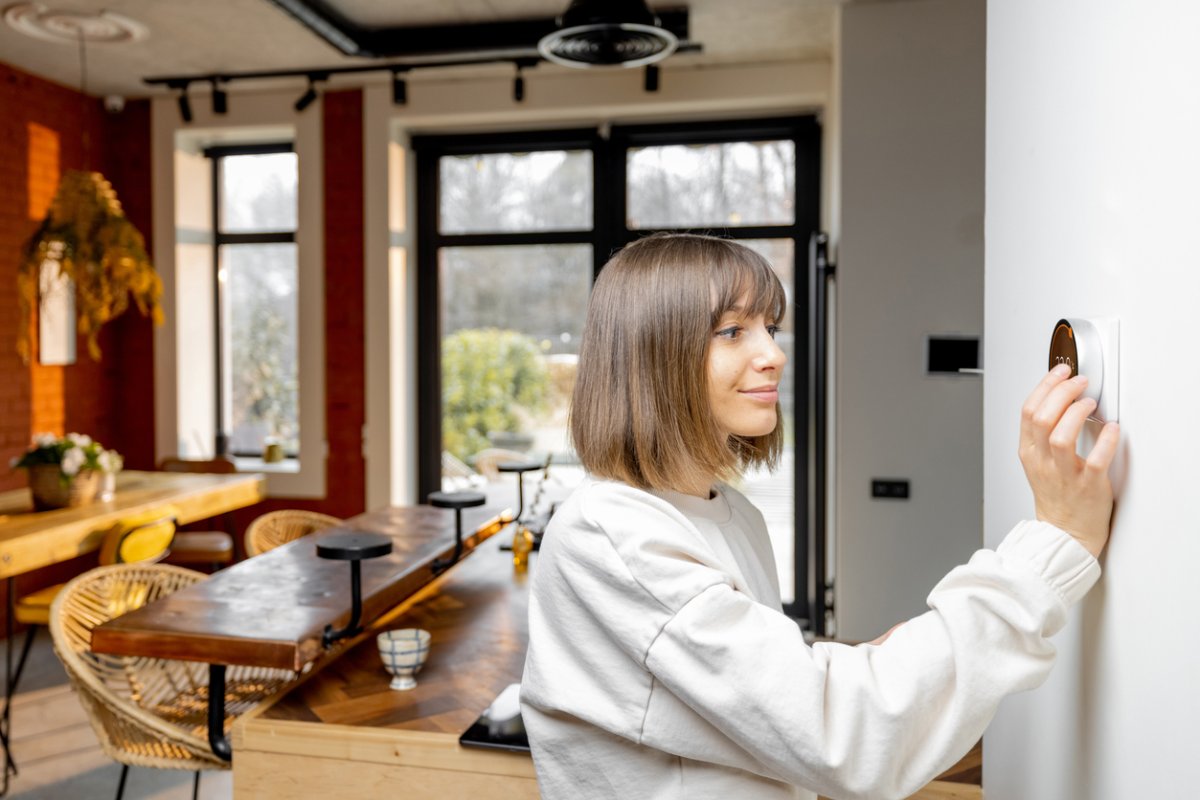
1. Indoor Air Temperature for Winter

Keeping your home comfortable during cold weather is important, but you don’t want to waste energy in the process and end up facing a huge utility bill. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, 68 degrees is the ideal wintertime setting for your thermostat. This temperature is high enough to keep the house warm, but not so high that you’ll be wasting energy. To keep your bills even lower and further reduce your energy footprint, drop the temperature by a few degrees when you go to sleep or before you leave the house. You can save up to 10 percent over the course of a year by setting your thermostat 7 to 10 degrees cooler than normal for at least 8 hours each day. If you don’t have one already, invest in a programmable thermostat so you can set schedules that match your typical comings and goings.
RELATED: How to Install a Thermostat
2. Indoor Air Temperature for Summer

For conserving energy over the summer, the ideal indoor air temperature setting is 78 degrees Fahrenheit. You can further reduce cooling costs and cut down on the amount of energy that is wasted by turning off the air conditioner, or at least increasing the temperature setting on the thermostat, whenever you leave your home. If you have a programmable thermostat, you can set it to automatically raise the temperature at times when you’re consistently away from the house.
RELATED: 14 Easy Ways to Increase Humidity in a Dry House
3. Indoor Humidity Level

High indoor humidity levels make it more likely that mold or bacteria will grow in your space. High humidity can also lead to condensation on floors and walls, and can cause problems for those suffering from allergies or asthma. On the flip side, however, excessively low indoor humidity levels can cause your nose and throat to feel dry and scratchy, and irritate your skin and eyes. According to the Mayo Clinic, an indoor humidity level between 30 and 50 percent is ideal. By keeping humidity levels within this range, you can avoid the problems associated with high and low humidity.
RELATED: Which Type of Water Heater Is Best for Your Home?
4. Hot Water Heater Temperature
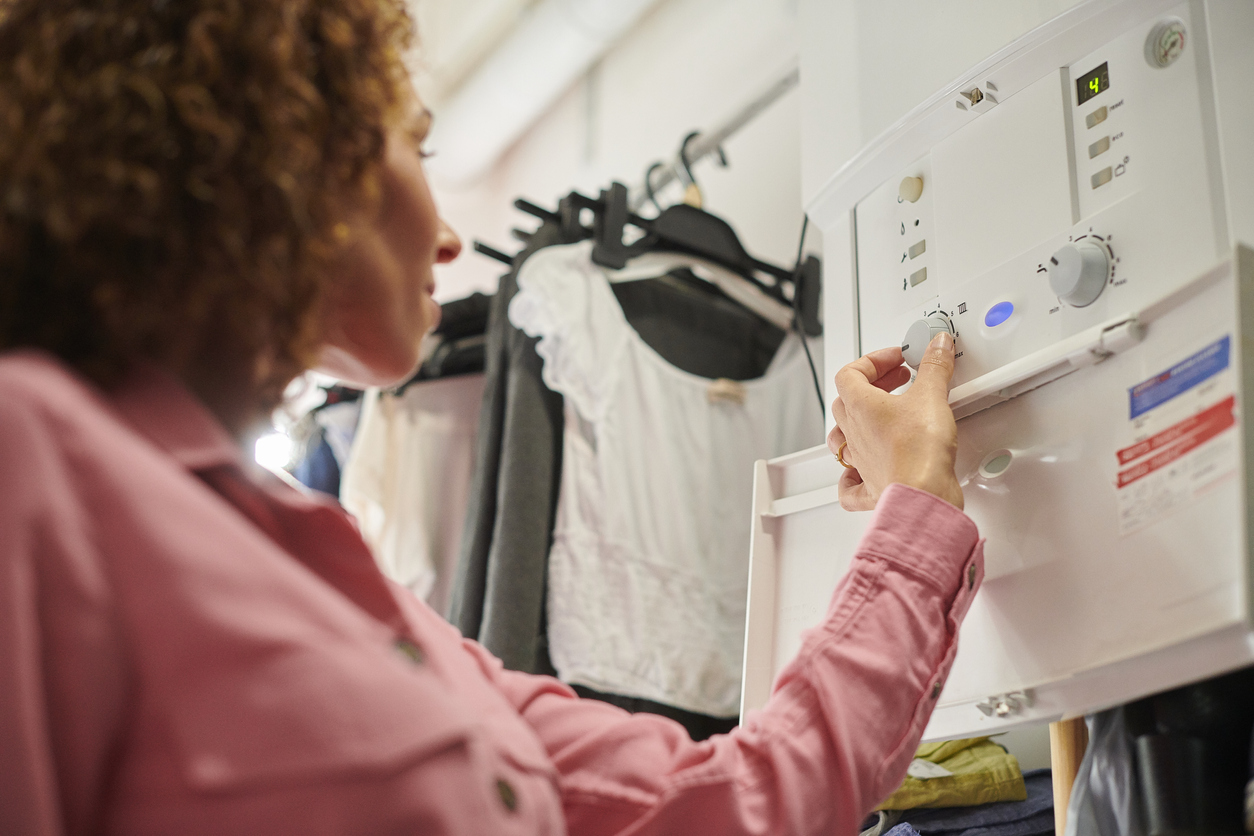

The U.S. Department of Energy recommends setting household water heater thermostats to 120 degrees Fahrenheit. If you haven’t adjusted your water heater’s factory setting, your unit may be set to a higher temperature, often 140 degrees Fahrenheit. Leaving it this high can cost you as much as $61 each year just for the energy required to reheat water that’s been sitting in the tank. When you factor in the amount of hot water used for showering, washing dishes, and doing laundry, an unnecessarily high setting could wind up costing you up to an additional $400 each year.
RELATED: What to Do When Your Refrigerator Is Not Cooling
5. Refrigerator Temperature
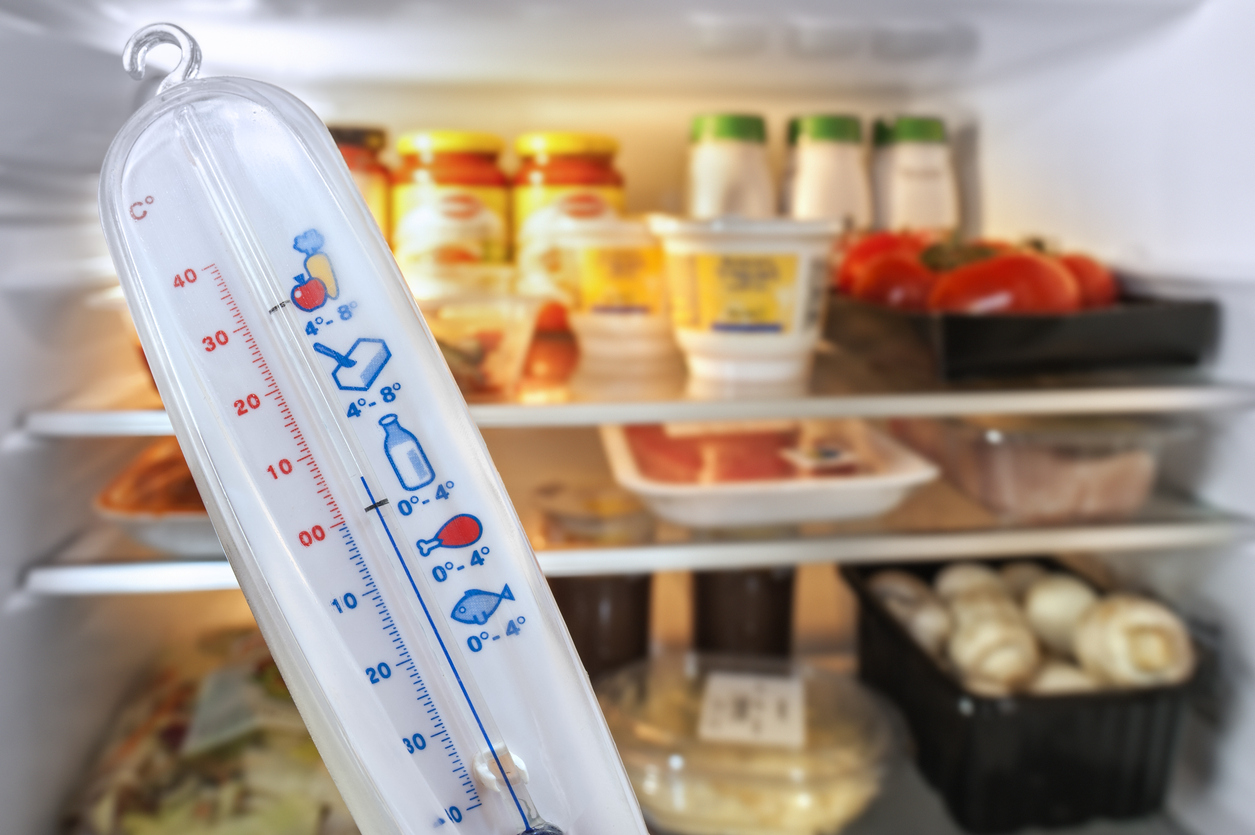

If your refrigerator is too warm, the food you’re storing inside it can spoil more quickly because bacteria multiply more rapidly when food is not properly chilled. Keeping your refrigerator too warm leads to food waste and exposes your family to the risk of food poisoning. According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, refrigerators should be set no higher than 40 degrees Fahrenheit to ensure foods are chilled properly and bacteria aren’t able to multiply and threaten your health. To monitor the temperature inside your refrigerator, it’s a good idea to invest in an appliance thermometer. While many models these days have built-in thermostats, some do not, and those that do may not be accurate.
RELATED: The Best Chest Freezers for Extra Cold Storage
6. Freezer Temperature
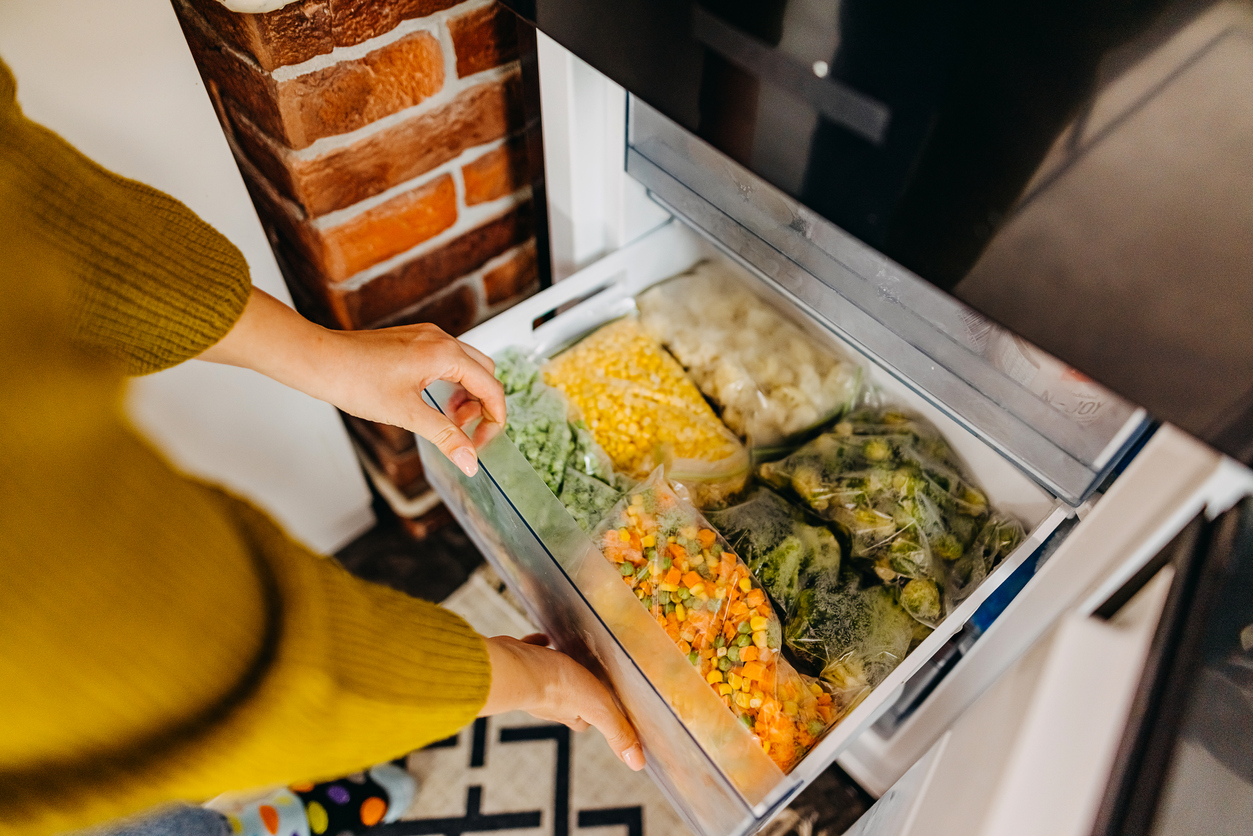

It’s important to set your freezer to the ideal temperature to help foods last longer and protect the health and safety of everyone in the home. According to the FDA, freezers should be set to 0 degrees Fahrenheit. Again, even if your unit has a built-in thermostat, use an appliance thermometer to verify that your freezer is actually maintaining the ideal temperature.
RELATED: Why Is My Carbon Monoxide Detector Beeping?
7. Placement of Carbon Monoxide Detectors
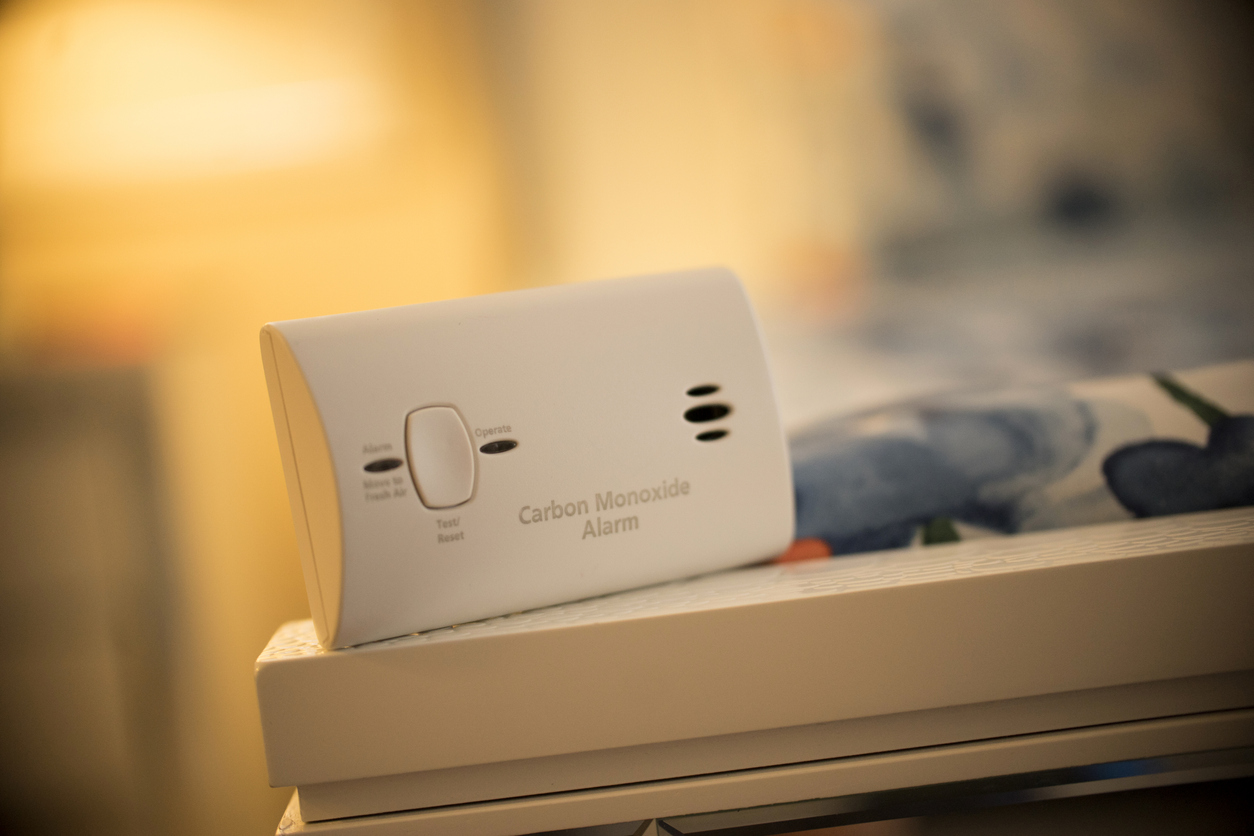
The Environmental Protection Agency recommends installing carbon monoxide detectors on each floor of a home. Proper placement is vital for ensuring that the units will operate as intended. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for installation, but in general if you’re installing a carbon monoxide detector on a wall, it should be placed at least 6 inches above the floor and at least 6 inches below the ceiling. If you want to install the detector on the ceiling, it must be a minimum of 6 inches away from the wall.
RELATED: How to Test for Radon in Your Home
8. Radon Cutoff Levels

Radon is present in both indoor and outdoor air, but while outdoor radon usually disperses quickly, high levels of radon indoors can have serious health consequences. It is estimated that exposure to radon gas causes about 21,000 lung cancer deaths each year, so it’s a good idea to monitor your home’s indoor air quality. If the radon level in your home is greater than or equal to 4 picocuries per liter (pCi/L), the EPA recommends having a radon mitigation system installed. Even if your home’s radon level falls between 2 pCi/L and 4 pCi/L, a radon mitigation system may still be the safest option.
RELATED: The Best Energy-Efficient Air Conditioners
9. Air Conditioner SEER Rating
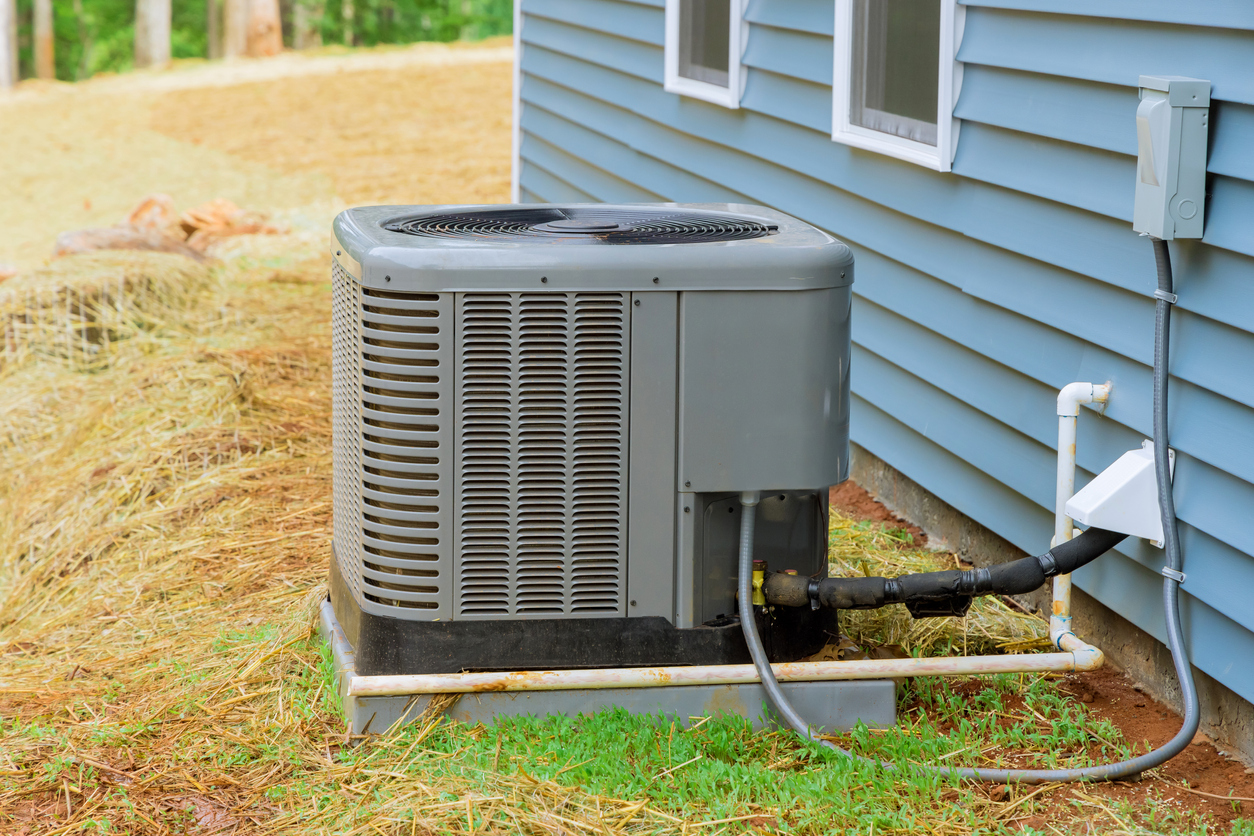

If you’re in the process of shopping for a new air conditioner or HVAC unit, then it is important to understand SEER ratings. SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings are calculated by dividing a unit’s cooling capacity by the amount of power it uses. Air conditioners with a higher SEER rating will be the most efficient options, keeping your home cool while minimizing energy use.
